In an era dominated by cloud computing and digital transformation, paper-based data recording continues to demonstrate surprising resilience and practical value across industries worldwide.
📊 The Unexpected Persistence of Paper in a Digital World
Despite predictions of a paperless society, paper-based record-keeping remains deeply embedded in modern business operations. From healthcare facilities to manufacturing plants, traditional documentation methods coexist alongside sophisticated digital systems. This isn’t simply organizational inertia—there are legitimate reasons why paper records maintain their foothold in contemporary workplaces.
The global business forms market, which includes paper-based recording systems, continues to generate billions in annual revenue. This sustained demand reflects practical needs that digital solutions haven’t entirely replaced. Understanding why paper persists reveals important insights about effective data management strategies that balance innovation with practicality.
🏥 Industries Where Paper Still Holds the Pen
Healthcare institutions represent perhaps the most visible sector where paper-based recording remains essential. Patient charts, consent forms, and medication administration records frequently exist in physical formats. The immediate accessibility of paper records during patient care, especially in emergency situations where digital systems might fail or slow down critical decisions, provides tangible advantages.
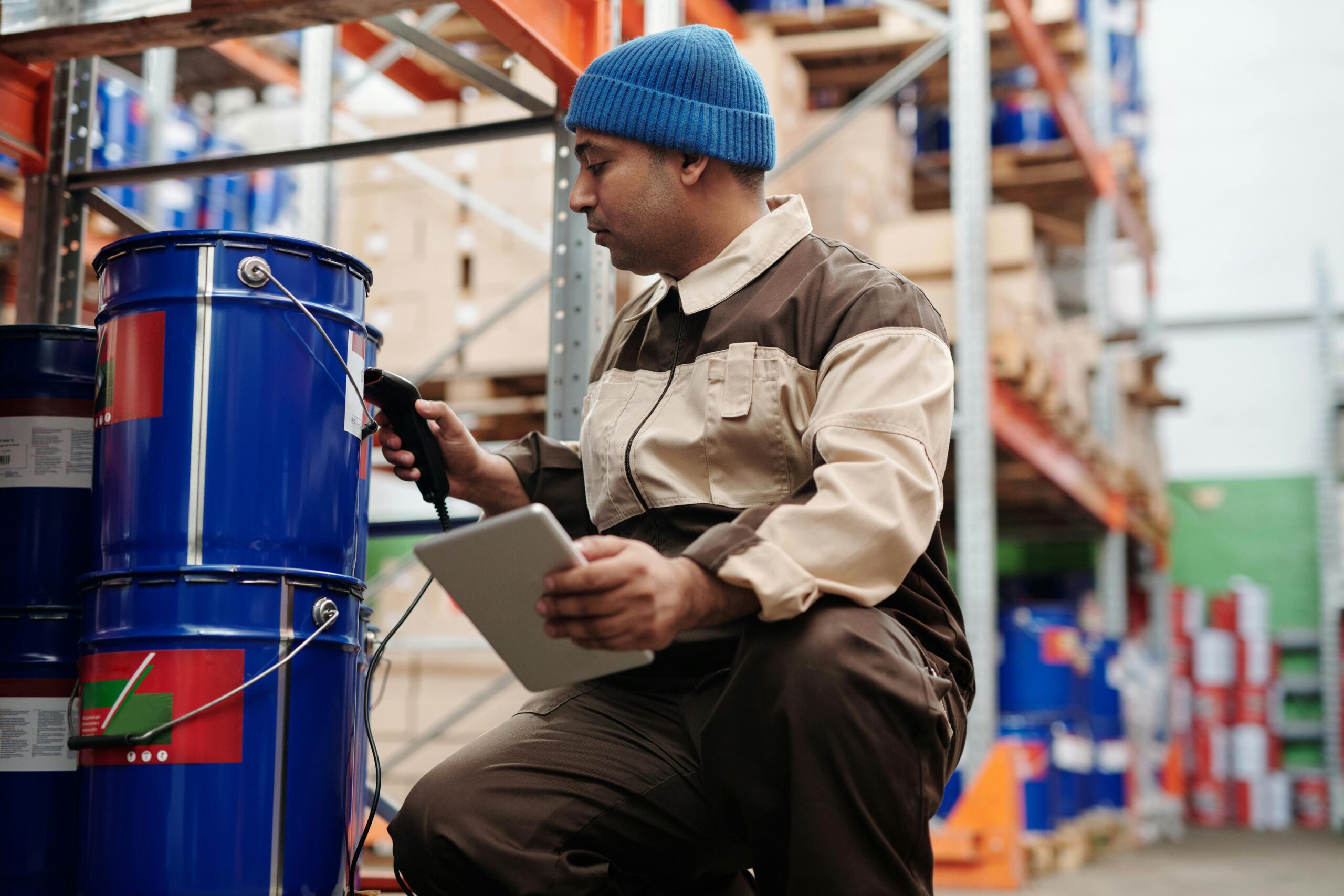
Manufacturing environments present unique challenges for digital devices. Factory floors with extreme temperatures, dust, moisture, or electromagnetic interference create hostile conditions for tablets and smartphones. Paper-based production logs, quality control checklists, and shift reports offer reliability that electronic devices cannot always guarantee in these demanding settings.
The legal sector maintains extensive paper archives for documents requiring original signatures and authentication. Courtrooms still operate predominantly with physical evidence and documentation. While digital copies exist, the legal weight of original paper documents continues to hold significance in many jurisdictions worldwide.
Construction and Field Operations
Construction sites exemplify environments where paper-based recording thrives. Site managers carry weather-resistant notebooks to document progress, safety inspections, and material deliveries. The rugged simplicity of paper withstands the harsh conditions that would quickly damage or complicate electronic alternatives. Field technicians across utilities, telecommunications, and service industries similarly rely on paper forms for immediate documentation without battery concerns or connectivity requirements.
💡 The Psychological and Cognitive Advantages of Paper
Research in cognitive psychology reveals that writing by hand activates different brain regions compared to typing on keyboards. This physical engagement enhances memory retention and information processing. Students who take handwritten notes consistently demonstrate better conceptual understanding compared to those who type notes digitally.
The tactile experience of paper creates a spatial memory component. People remember where information appeared on a page—top, bottom, left margin—creating mental landmarks that aid recall. Digital documents lack this physical dimension, making information retrieval sometimes less intuitive despite search functions.
Paper records provide an unmediated relationship with information. There’s no interface between the user and the data—no loading screens, software crashes, or compatibility issues. This directness reduces cognitive load and eliminates technological friction that can impede workflow efficiency.
Creative Thinking and Problem-Solving
Designers, architects, and creative professionals often begin projects with paper sketches. The freedom to draw, annotate, and explore ideas without software constraints facilitates innovative thinking. Paper supports non-linear thought processes that don’t conform to predetermined digital templates or structured input fields.
🔒 Security and Privacy Considerations
Paper-based records offer inherent security advantages in specific contexts. They cannot be remotely hacked, don’t create digital footprints, and leave no metadata trails. For highly sensitive information, physical documents stored in secured locations provide a level of protection against cyber threats that digital systems must constantly defend against.
The phenomenon of “air-gapping”—maintaining critical information completely disconnected from networks—relies on paper documentation. Government agencies, financial institutions, and research facilities sometimes deliberately use paper records for their most sensitive data to eliminate remote access vulnerabilities entirely.
However, paper records face different security challenges. Physical theft, fire, water damage, and simple misplacement create risks that digital backups can mitigate. The optimal approach often involves hybrid systems that leverage the security benefits of both mediums while compensating for their respective vulnerabilities.
🔄 Hybrid Systems: The Best of Both Worlds
Progressive organizations don’t view paper and digital as competing alternatives but as complementary tools. Hybrid record-keeping systems capture advantages from both approaches while minimizing individual limitations. These integrated methodologies represent the future of practical data management.
Medical practices increasingly employ hybrid workflows where clinicians complete paper forms during patient interactions, maintaining eye contact and rapport. Support staff then digitize these records into electronic health systems, combining the interpersonal benefits of paper with the storage and retrieval advantages of digital databases.
Document Scanning and Digitization Workflows
Modern scanning technology enables rapid conversion of paper records into searchable digital formats. Organizations maintain paper originals for legal compliance while creating digital copies for daily operations. This approach satisfies regulatory requirements without sacrificing operational efficiency.
Mobile scanning applications have democratized digitization, allowing field workers to capture paper documentation immediately and transmit it to central systems. This bridges the gap between paper’s field convenience and digital centralization requirements.
📱 Mobile Apps Supporting Paper-Digital Integration
Numerous applications facilitate the transition between paper and digital formats. Scanner apps use smartphone cameras to capture documents with automatic edge detection, perspective correction, and enhancement. These tools transform phones into portable digitization stations that support paper-based field recording.
Note-taking applications that recognize handwriting bridge analog and digital worlds. Users write naturally on paper or tablets, and intelligent character recognition converts handwritten content into searchable, editable digital text. This preserves the cognitive benefits of handwriting while enabling digital organization and accessibility.
🌱 Environmental Sustainability Perspectives
The environmental impact of paper versus digital record-keeping presents a nuanced comparison. While paper consumption involves tree harvesting and physical waste, digital infrastructure requires substantial energy for data centers, device manufacturing, and electronic waste disposal.
Responsible paper use with recycled materials and proper recycling programs can achieve sustainability comparable to digital alternatives. The environmental equation depends on usage patterns—digital systems become more efficient at scale, while paper may be more sustainable for limited, short-term applications.
Organizations committed to environmental responsibility evaluate their specific circumstances rather than assuming digital automatically equals greener. Factors include document longevity requirements, access frequency, redundancy needs, and disposal methods for both paper and electronic equipment.
Sustainable Paper Practices
Forest certification programs ensure paper products come from responsibly managed sources. Businesses can specify recycled content percentages and support closed-loop recycling systems. Digital printing reduces waste from pre-printed forms by enabling on-demand production of only needed quantities.
⚖️ Regulatory Compliance and Legal Requirements
Many industries operate under regulations specifically requiring paper documentation or original signatures. Financial institutions must maintain certain records in tamper-evident formats. Healthcare regulations specify retention periods and authentication methods that sometimes necessitate physical documents.
Legal discovery processes frequently involve paper records that carry evidentiary weight differently than electronic documents. Chain of custody requirements, authentication standards, and admissibility criteria vary between physical and digital documentation across legal jurisdictions.
Understanding these regulatory landscapes helps organizations design compliant record-keeping systems. Compliance teams must navigate requirements that sometimes explicitly mandate paper, permit either format, or specifically require digital retention with specific security standards.
🎯 Practical Strategies for Effective Paper-Based Recording
Organizations maintaining paper records benefit from systematic approaches that maximize efficiency and reliability. Standardized forms with logical layouts reduce recording errors and improve information completeness. Clear labeling conventions and consistent filing systems enable quick retrieval when needed.
Training staff on proper documentation techniques ensures quality and consistency. This includes legible handwriting standards, complete information capture, appropriate correction methods, and proper handling to maintain document integrity over time.
Quality Control and Verification
Implementing review processes catches errors before paper records enter permanent archives. Supervisory review, dual verification for critical data, and periodic audits maintain accuracy standards. These quality measures prove especially important since paper records lack the validation rules and automated checks available in digital systems.
🚀 Innovation in Paper-Based Technology
Paper technology itself continues evolving. Smart paper with embedded sensors can detect when writing occurs and transmit data wirelessly to digital systems in real-time. This creates synchronized paper-digital records automatically without manual scanning or transcription.
Specialized papers resist water, chemicals, and extreme temperatures, extending usability in challenging environments. These engineered materials maintain paper’s simplicity while addressing durability limitations that previously necessitated digital alternatives.
Digital pens equipped with cameras track handwriting on regular paper and simultaneously create digital versions. Users experience natural paper writing while automatically generating backup digital records, eliminating the choice between paper’s benefits and digital’s advantages.
🔍 When Paper Makes the Most Sense
Certain situations clearly favor paper-based recording. Brainstorming sessions benefit from large paper sheets that groups can annotate collectively. Quick reference materials like emergency procedures are more accessible as laminated cards than buried in digital systems requiring navigation.
Temporary records with short retention requirements don’t justify database entry overhead. Visitor logs, daily task lists, and scratch calculations serve their purpose efficiently on paper without creating digital clutter.
Backup and redundancy strategies wisely include paper copies of truly critical information. When systems fail—and they inevitably do—paper provides failsafe access to essential data without dependency on electricity, networks, or functioning hardware.
Personal Productivity Applications
Individuals often discover paper planners, journals, and notebooks support personal organization better than digital equivalents. The physical act of writing commitments enhances accountability. The absence of digital distractions when using paper tools improves focus and follow-through on priorities.
🌐 The Future Landscape of Record-Keeping
The trajectory forward involves sophisticated integration rather than paper’s elimination. Artificial intelligence will enhance paper-digital transitions through improved handwriting recognition and automated data extraction from scanned documents. Machine learning algorithms will categorize and route paper-sourced information to appropriate digital systems with minimal human intervention.
Augmented reality may overlay digital information onto physical paper documents, creating enhanced hybrid experiences. Users could view historical annotations, related digital files, or real-time updates while examining paper records through AR-enabled devices.
Blockchain technology might authenticate paper documents through cryptographic verification, combining paper’s tangibility with digital security assurances. This could resolve longstanding tensions between paper’s accessibility and concerns about authenticity and tampering.

✍️ Embracing Practical Wisdom Over Technological Fashion
The persistence of paper-based record-keeping reflects practical wisdom rather than technological backwardness. Effective data management requires matching tools to specific requirements rather than uniformly applying the newest solutions. Paper excels in particular contexts that digital alternatives serve poorly or at disproportionate cost and complexity.
Organizations achieving operational excellence recognize that revolutionary approaches sometimes mean intelligently preserving proven methods alongside innovations. The future belongs not to paper or digital exclusively, but to thoughtful integration that leverages each medium’s strengths while compensating for weaknesses.
As technology continues advancing, paper’s role will evolve but likely never disappear entirely. Its simplicity, reliability, and cognitive benefits ensure continued relevance across applications where these characteristics matter most. The revolution in record-keeping isn’t replacing paper—it’s discovering how paper and digital systems work together more effectively than either approach alone.
Success in modern record-keeping demands moving beyond either-or thinking toward integrated strategies. This balanced perspective acknowledges paper’s limitations without dismissing its genuine advantages. Organizations adopting this nuanced approach position themselves to benefit from both traditional reliability and digital innovation, creating resilient systems prepared for whatever challenges tomorrow brings.
Toni Santos is a data analyst and predictive research specialist focusing on manual data collection methodologies, the evolution of forecasting heuristics, and the spatial dimensions of analytical accuracy. Through a rigorous and evidence-based approach, Toni investigates how organizations have gathered, interpreted, and validated information to support decision-making — across industries, regions, and risk contexts. His work is grounded in a fascination with data not only as numbers, but as carriers of predictive insight. From manual collection frameworks to heuristic models and regional accuracy metrics, Toni uncovers the analytical and methodological tools through which organizations preserved their relationship with uncertainty and risk. With a background in quantitative analysis and forecasting history, Toni blends data evaluation with archival research to reveal how manual methods were used to shape strategy, transmit reliability, and encode analytical precision. As the creative mind behind kryvorias, Toni curates detailed assessments, predictive method studies, and strategic interpretations that revive the deep analytical ties between collection, forecasting, and risk-aware science. His work is a tribute to: The foundational rigor of Manual Data Collection Methodologies The evolving logic of Predictive Heuristics and Forecasting History The geographic dimension of Regional Accuracy Analysis The strategic framework of Risk Management and Decision Implications Whether you're a data historian, forecasting researcher, or curious practitioner of evidence-based decision wisdom, Toni invites you to explore the hidden roots of analytical knowledge — one dataset, one model, one insight at a time.